In this article, Kashish Khattar discusses ten banking transactions every banking lawyer should know about.
Syndicate Loans
When a large group of lenders wants to collectively extend a loan to a single borrower, using similar terms and conditions, documentation etc. administered by a common agent, it is called a syndicated loan. The group of lenders is called “syndicate”.
Generally, this loan is provided to corporations and government bodies because the amount to be lent is huge. Syndicated loans are primarily given by the banks, but these days a variety of investors are also involved in this loan lending institution such as mutual fund, insurance companies, pension plans and hedge funds etc.
Clik here to view.
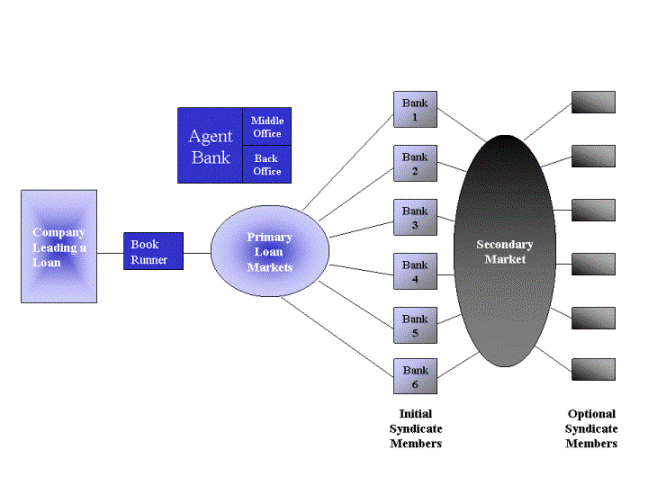
Consortium Finance
Typically, banks finance loans according to their lending policy. Sometimes, when a single banker is not able to finance a single customer. When a situation like this arises, banks jointly grant loans and advances to a customer. This kind of financing is called consortium financing. When two or more banks come together, it is called consortium financing. In this situation, which is based on an agreement between banks of the consortium and group will select one banker as the ‘Lead Bank’. Its functions range from arranging meetings between the member banks and active involvement in credit appraisal, obtaining legal documents etc.
Banks tend to loan consortium finance on account of various factors, which can be:
- Various regulatory requirements.
- Restrictions on single and group borrower’s limits.
- Part of risk management and diversification policy of banks.
- At the request of a borrower.
There is a subtle difference between Syndicated Loan and Consortium Finance, which can be briefly understood as every syndicate is a consortium, but every consortium is not a syndicate. The art of understanding the difference lies in the technicalities of their individual operations, procedures, relationships and legal complexities. But the key difference in these banking transactions is that with a consortium the lender will be able to repay one bank and fail to repay another. In the case of a syndicate, there is only one loan. The borrower would default on the whole loan which will land him in legal trouble.
Further reading on the difference, here.
Bridge Loans
Bridge loans are short-term loans which are granted typically to industrial undertakings to meet their urgent and essential needs during the period when formalities for availing of the term loans sanctioned by financial institutions are being fulfilled or necessary steps are being taken to raise the funds from the capital market.
These loans are granted by banks or by financial institutions themselves and are automatically repaid out of an amount of the term loan or the funds raised in the capital market.
The key guidelines to sanction Bridge Loans as notified by RBI should include the following aspects –
- Security should be for the loan.
- There should be compliance with the individual or group exposure norms.
- The value of the outstanding bridge loan (or the limit sanctioned, whichever is higher) during the year
- Ensuring the end use of bridge loan, as to where is the loan going to be used.
- The maximum period of the bridge loan to be one year only.
Clik here to view.

Letter of Credit
A letter of credit (“LC”) is issued by the bank at the request of its customer (Importer) in favour of the beneficiary (Exporter). It is an undertaking by the bank, informing the beneficiary that the documents under the LC will be honoured if the beneficiary submits all the paperwork as per the terms and conditions. Banks are mainly involved in LC to avoid default in payments, to facilitate trade and also enable the exporter and importer to receive and pay for the goods sold and bought.
Bill Purchasing and Discounting
It is basically is an exercise to reduce the risk. Bill discounting is a process where the seller recovers an amount of sales bill from the financial broker before it is due. A broker charges a fee for this service. It is like selling the bill to a discounting company before the due date of payment at a price which is relatively less than the bill amount. The difference between the bill amount and amount paid is the fee of the discounting company. It will mainly depend on the period left before the payment date and the perceived risk.
It is a win-win situation for both the parties in the transaction, ie, the buyer and seller. The seller gets his money instantly on payment of a small charge and gives the buyer, a credit period. It is an easy way of getting finance, requiring no sanctions.
Mortgage and Hypothecation
Both the terms talk about a secured loan for the creditor. Where Mortgage is basically said to be a charge against an immovable property. Which may include – Land, Building, Warehouse, etc. A mortgage is typically against something that is attached to the earth or deriving benefits from the earth. There are 6 types of mortgage defined in the Transfer of Property Act, 1882 which are Simple, English, Usufructuary, Anomalous, Deposit by Title Deeds and Conditional Sale. Delivery depends on the type of mortgage between the parties.
Hypothecation is a charge against movable property mostly cars, account receivables, and stocks etc. Hypothecation is defined under the SARFAESI Act, 2002 as charge in or upon any movable property, existing or future, created by a borrower in favour of a secured creditor without delivery of possession of the movable property to such creditor, as a security for financial assistance and includes a floating charge and crystallisation of such charge into a fixed charge on movable property.
Revolving Credit
Revolving credit is mainly defined as having a line of credit where the borrower just has to pay a commitment fee to a financial institution such as a bank to borrow money and is then allowed to use the funds whenever they are needed. They are typically used for operating some big projects or purposes. The amount can vary from a month to month basis. Revolving credit is usually taken out by corporations or high net worth individuals. The maximum amount of revolving credit is called the credit limit. The bank which is the main financial institution in these kinds of transactions reach an agreement over the commitment fee, interest expenses and carry forward charges for consumer accounts.
Revolving credit is such a huge advantage for people or companies that face sharp fluctuations in cash flow and face unexpected expenses. The convenience and the flexibility account for the high rate of interest which is charged by the banks. They are different than instalment loans as they require a fixed number of payments over a period of time whereas the revolving credit only requires payment of the applicable interest and the fee.
Overdraft Facilities
An overdraft facility can be understood in a simple way, it is a general credit agreement which is made with a financial institution, such as a bank that permits the account holder to use, withdraw more than the amount that they really have without exceeding a specified maximum negative balance in their agreement.
Usually done by individuals and small-medium sized enterprises who can have a short-term cash flow problems. Typically, the negative balance needs to be repaid in a month’s time.
Project Finance
Project Finance is basically the long-term financing of an industrial, infrastructural or a public services project based upon non-recourse or limited recourse of financial structure. The project debt and equity which is used to finance the project are paid back from the cash flow generated by the project itself. It is a kind of a loan structure, which relies mainly on the project’s cash flow. With the project’s assets, rights and liabilities are considered as collateral.
These kind of loans are mainly non-recourse, which are protected by the assets of the projects and are paid entirely from the cash flow generated from the project. Instead of being sponsored by the general assets of the sponsors or their creditworthiness. They mainly are fancy to the private sector as they can fund these major projects off balance sheet. Which means, that these assets won’t come on the balance sheet of the company, but they are effectively assets or liabilities of the company.
A project finance structure mainly a build, operate and transfer project has some essential key elements. A special purpose vehicle is constituted for project financing. The sole purpose of the company is to carry out the project by subcontracting various construction and operations agreement. The main attraction of project financing is that it remains off-balance sheet for the sponsors and the government.
A diagram showing project financing of a Wind Farm Project.
Clik here to view.

Term Loan
It can be simply understood as a loan for a specific amount which has a specific repayment schedule and a fixed or floating interest rate over it. Meaning, it can be paid in lump sum or in suitable amount according to the agreement. A loan is known as a Demand loan if it has to be repaid within three years. If the loan’s term is three or more than three years it is known as a Term Loan.
They are mainly given to the manufacturing, trading and service sectors which require funds for buying various fixed assets, such as land, building, machinery, and electrical installation etc. Repayment of term loans depends mainly on the firm’s capacity to produce goods or services by the fixed assets financed by the bank.
Acknowledgement:
Banking Laws and Practise ICSI
Investopedia
Wikipedia
The post 10 Banking Transactions Every Banking Lawyer Should Know About appeared first on iPleaders.
Image may be NSFW.Clik here to view.